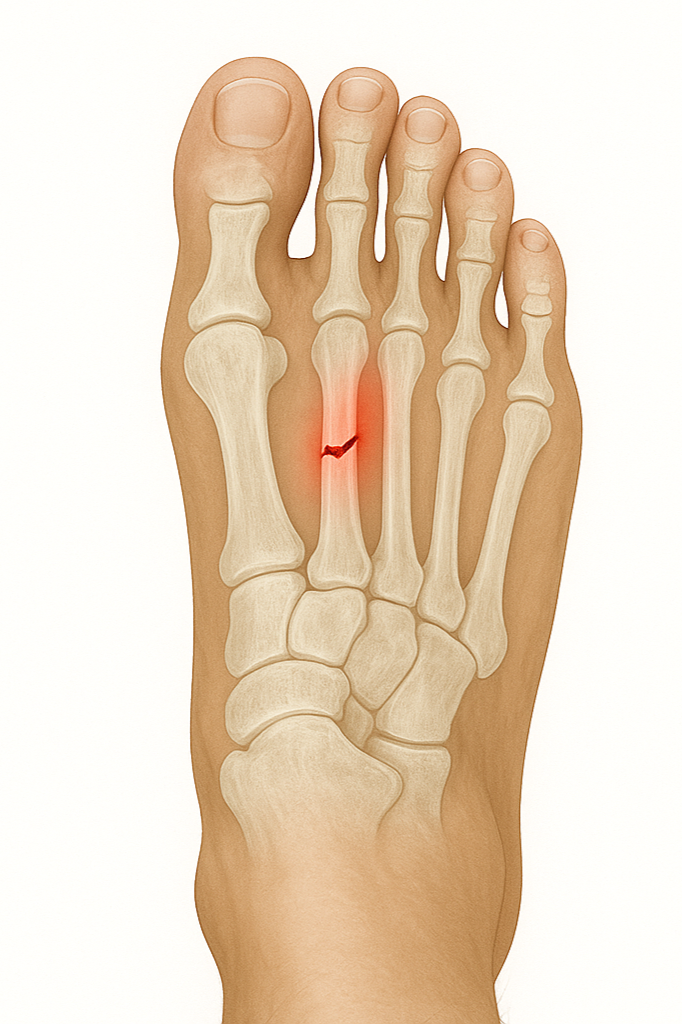
Stress Fracture
A stress fracture is a small crack in the bone caused by overuse or repetitive stress. It most often occurs in the weight-bearing bones of the foot and lower leg. When muscles are overworked and can’t absorb impact, the stress is transferred to the bone, leading to a fracture.
-
Rapid increase in exercise or training intensity
Running or jumping on hard surfaces
Wearing improper or worn-out footwear
Overtraining without adequate rest
Sports with repetitive foot impact (basketball, tennis, gymnastics)
👩🦰 Women are at higher risk, especially athletes with the “female athlete triad,'“ a combination of poor nutrition, irregular menstrual cycles, and low bone density.
-
Localized pain in the foot or ankle that worsens with activity and improves with rest
Swelling, bruising, or tenderness at a specific point
Difficulty bearing weight or continuing sports activity
-
Rest and activity modification – stop activities that worsen pain
Ice and elevation – to reduce swelling and inflammation
Supportive footwear – avoid worn or unsupportive shoes
Protective footwear or walking boot to reduce stress on the fracture
Casting or bracing to immobilize the foot if needed
Crutches to avoid weight-bearing until the fracture heals
If the fracture does not heal with conservative care, surgery may be needed. This involves using pins, screws, or plates to stabilize the bone until healing occurs.
-
Start new sports or exercise programs slowly and progress gradually
Cross-train – alternate activities (e.g., run some days, cycle or swim on others)
Wear proper, supportive shoes and replace worn footwear regularly
Maintain a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D
Listen to your body! Iff you have persistent footpain, rest and seek evaluation
Disclaimer: The information on this website is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor with any questions about your health.